
In This Article, You Will Read:
Introduction: Brief description of the functionality of locomotive traction motor
A locomotive is a self-propelled vehicle that runs on rails and uses for moving or pulling trains. A traction motor helps the locomotive to move forward.
Traction motors use in locomotives for the propulsion of a vehicle. Locomotive traction motor parts use electrically powered rail vehicles and other electric vehicles such as elevators, roller coasters, and locomotives with electrical transmission systems like diesel-electric locomotives and battery electric vehicles.
Locomotive traction motor specifications are mentioned below in the table:
Rated power [kW] | 130 to 1,630 |
Rated speed [rpm] | 240 to 2,280 |
Maximal operating speed [rpm] | 1,460 to 4,300 |
Rated torque [Nm] | 2,920 to 12,990 |
Cooling | Forced ventilated / open circuit cooled |
Weight [kg] | 1,630 to 2,980 |
Currently, locomotive traction motors classify into two categories:
- 1Pure electric
- 2Diesel locomotives
Locomotive traction motor parts classify based on two criteria: form and mounting configuration.
In the locomotive industry, there are two different types of traction motors:
- 1DC traction motors
- 2AC traction motors with Variable Frequency Drives (VFD)
For locomotives, AC traction is a significant improvement over the old DC systems.
AC traction motors have much higher reliability and maintenance standards than DC traction motors, with adhesion levels up to 100 percent higher than DC.
You may also like: AC vs DC traction motors
Contact our experts
Don’t hesitate to contact us!
The necessity of maintenance for locomotive traction motor parts
Traction motors for locomotives play a crucial part in the rail industry, and they must be well-maintained and in good working order to avoid underperformance or sudden breakdowns.
Our company has extensive rail industry expertise, including emergency maintenance, fault finding, rewinds, and overhauls on all forms of AC and DC traction motors, generators, and related machinery.
When we receive a traction motor for overhaul, we run a series of checks to ensure it’s in good working order.
Our basic traction motor overhaul procedure is as follows:
- test to see if there are any acute problems.
- Disassembled test for any component distortion or wear.
- The locomotive traction motor parts are disassembled, and steam washed.
- Bearings are substituted after they have been removed.
- clean and repaint to look brand new.
- reassemble and test one more time.
The most important parts in locomotive traction motor :
1Commutator
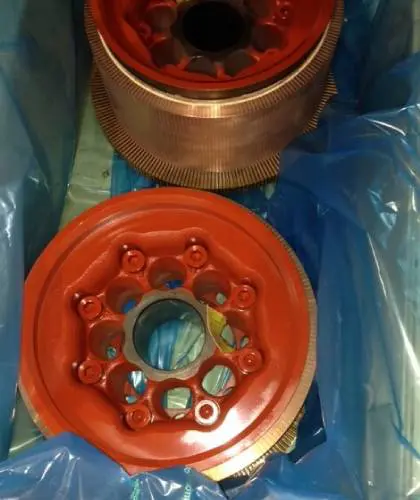

A commutator’s job is to invert the DC input wave into an AC wave in the armature winding. It comprises a series of short wedge-shaped segments of high conductivity hard-drawn copper separated from one another by mica or mica nite separators with a thickness of around 0.8 mm to prevent brush jumping and spark. (Wikipedia)
The commutator segments are attached to a V-cone-shaped insulated steel cylinder. The assembly is pulled into the shaft and pressed into place.
When the Commutator diameter is roughly equal to the armature diameter, the ends of the armature coils are directly soldered to the Commutator frame.
2Armature
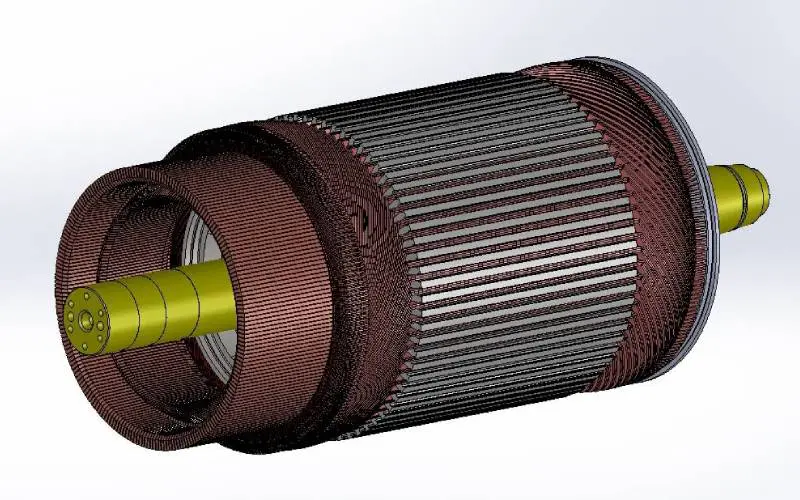
It is the locomotive traction motor spinning member, made up of a series of copper conductors that have been carefully arranged and attached to create a closed winding.
Slots, teeth, winding, and the core make up the armature. Depending on the number of poles and speed (f=PN/120), the spinning armature is exposed to an alternating flux with a frequency of 20 to 50 Hz.
The loss due to eddy currents is proportional to the thickness squared. As a result, the armature comprises 0.4 to 0.5 mm thick magnetic steel laminations separated by a thin layer of class H varnish.
The armature shaft is keyed to the punching. To boost ventilation, the core has longitudinal ventilating ducts. The laminations are held in place by a cast steel armature head at the pinion end and released steel armature sleeves at the other end, held on the shaft by a fixed ring and retaining ring at the pinion end.
3Main coils 1,2,3 & 4 in locomotive traction motor parts
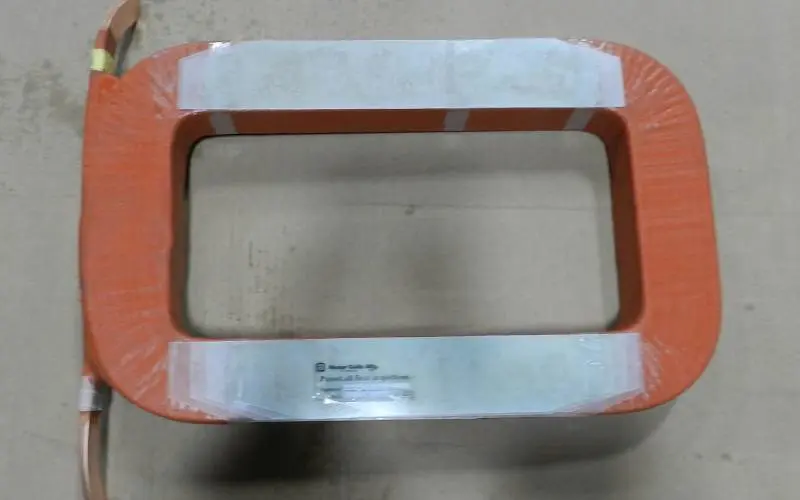

A coil assembly with electrically linked first and second outer windings and a third inner winding. The number of turns in the outer windings is roughly half that of the inner winding. The outer windings are all identically wound and have a terminal that extends outwards.
4Poles 1,2,3 & 4 in locomotive traction motor parts
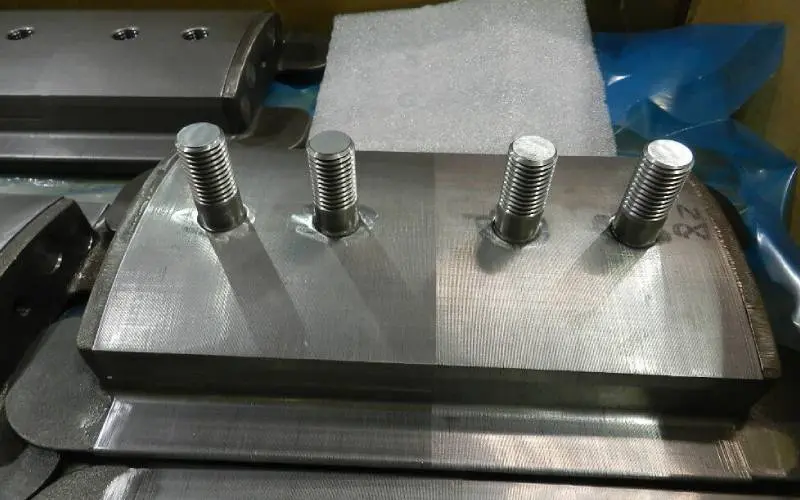

A 4-pole motor produces 3.0 ft-lbs of torque per horsepower, while a 2-pole engine produces 1.5 ft-lbs of torque per horsepower.
A 4-pole motor spins at 1800 rpm at 60Hz, while a 2-pole motor spins at 3600 RMP. As a result, the 4-pole engine has higher efficiency and produces more torque per unit of volume and weight.
5Interpole assembly
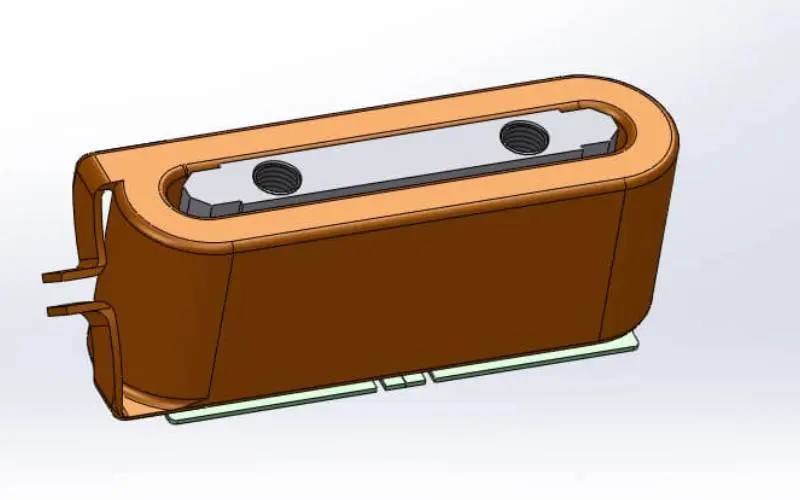
6CE Bearing Cover in locomotive traction motor parts
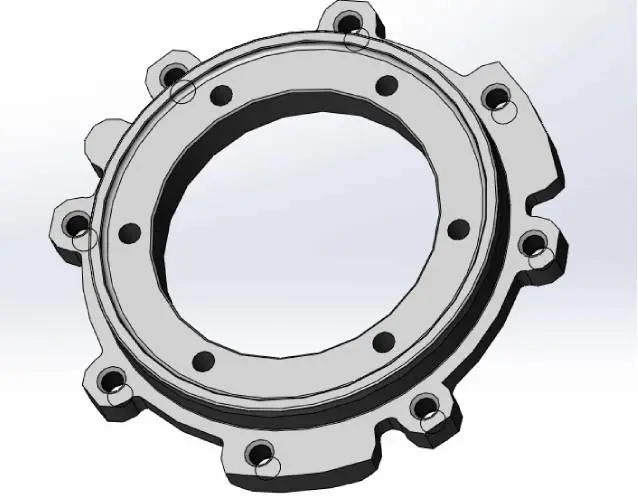

Using the tapped hole for pulling out, remove the CE, end bell, and outer ring of roller bearing (bearing bracket) from the magnet base. When handling the bearing bracket, pay close attention.
7PE Bearing Cover in locomotive traction motor parts
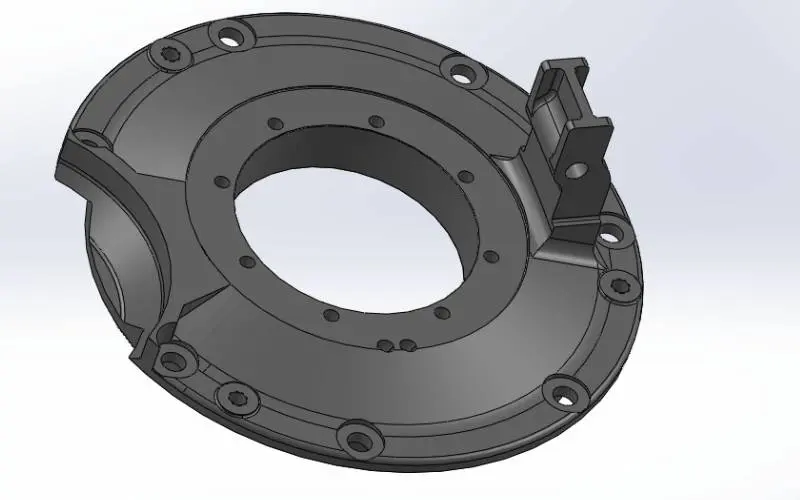
Place a steel bar (20 mm dia) within the end shield bolt hole and extract the end bell crosswise, raised and supported by a crane, to disassemble the end shield from the dismounted armature.
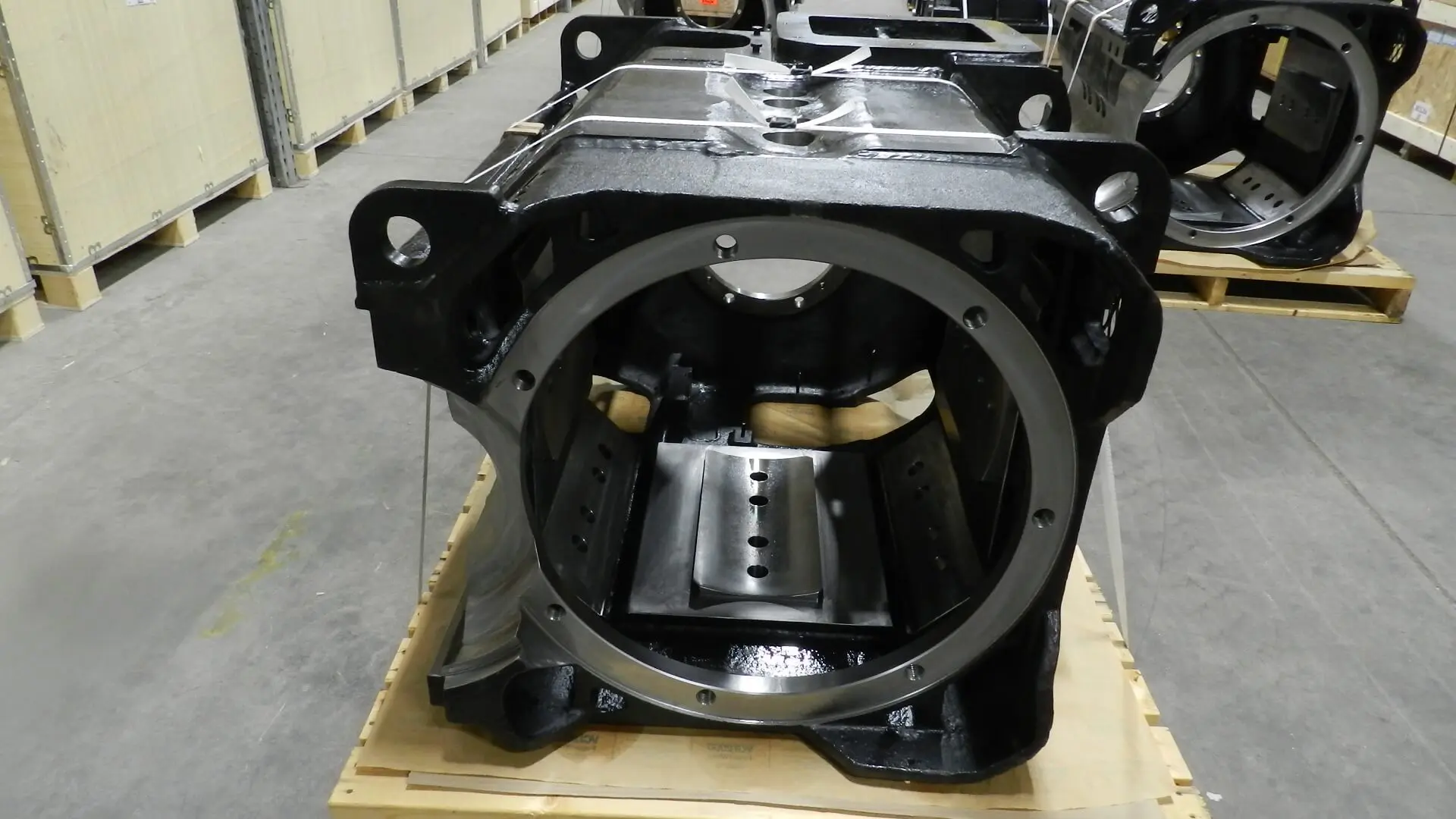
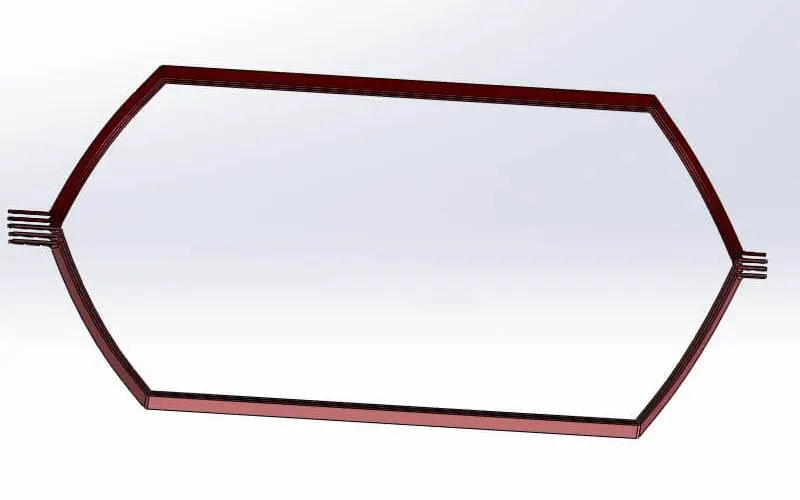
8Traction motor Frame
9Traction Motor Insulation Kit
In DC machines, the armature windings are situated on the rotor, and in AC machines, they are located on the stator. Vacuum-pressure impregnation (VPI) or resin-rich (RR) technology can be used in the insulation. Silicone, unsaturated Polyesterimide, epoxy, or polyester can be used as the main-wall insulating resin.
10End Bell in locomotive traction motor parts
Both ends of the pinion and the commutator have an end bell. Roller bearings on both sides support the armature.
A grease nipple and bearing covers also provided to lubricate the bearings during routine maintenance and shield them from dust and foreign objects.
11Pinion
It’s made of high-speed carbon steel and shrink-wrapped around the armature head. This pinion has 15 or 21 teeth, is directly geared to the wheel set’s gear, and is responsible for driving the wheelset and, eventually, the locomotive traction motor parts.
You may also like: locomotive traction motor pinion
Conclusion
While AC traction motors are widely used in today’s locomotive industry, it’s still necessary to know the necessity of maintaining both AC and DC traction motor technologies and all traction motor parts plus traction motors 11 products.
We assume this report has included all of the essential topics. If you have any more concerns about the necessity of maintenance AC and DC traction motors, please contact us for a quotation.
Contact our experts
Don’t hesitate to contact us!




